Ball Valve VS Check Valve: Which is the best?
Industrial Valves are critical components of various industrial equipment. The Industrial Valves Market Size was valued at USD 73.0 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach USD 90.5 billion by 2026. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.4% during the forecast period. (Souce: MarketsandMarkets™)
With the wide variety of valve options on the market, finding one that provides the best results in your application can be a challenge. There are different types of industrial valves, including ball valves, gate valves, globe valves, check valves, plug valves, needle valves, butterfly valves, pressure relief valves, and so on.
The ball valve vs check valve comparison guide will help to choose which one is the best for us.
What is Ball Valve?

Ball valve is mainly used in pipeline for cutting off, distributing and changing the flow direction of medium, it only needs to close tightly with 90 degree rotation operation and very small turning torque.Because of their relatively simple design, ball valves are low maintenance, have a long service life, and, if used properly, leak very little.
What is Check Valve?

Check valves are automatic one-way valves that are designed to allow fluid flow in one direction only. The primary function of a check valve is to stop the programmed flow of the system from flipping, which could damage the equipment or destroy the program. One-way directional valves are another name for industrial check valves.
Types Differences between ball valve and check valve
Main Types of Ball Valve
- single body valve
- three-piece body valve
- welded valve
- floating ball valves
- trunnion valves
Main Types of Check Valve
- duckbill check valves
- ball check valves
- swing check valves
- butterfly check valves
- wafer check valves
- lift-type check valve
Material Differences between ball valve and check valve
Main Materials of Ball Valve
The common materials of ball valves are: cast iron, cast steel, stainless steel, and copper.
- Cast iron ball valves are mostly used in industrial pipelines, over normal temperature water, steam, air, oil and other media.
- Stainless steel ball valves are mostly used in medium and high pressure pipelines, with stronger temperature resistance, stainless steel ball valves are mostly used in chemical, petrochemical, smelting and other industries.
- Copper ball valve mainly refers to the threaded connection of the copper ball valve, the diameter of this type of valve is small, but also our daily life is more common in a valve, more installed in the HVAC pipeline, over hot water use.
Main Materials of Check Valve
- Stainless steel check valve is applicable to the pipeline of petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical, fertilizer, electric power industry and other working conditions, and the applicable medium is water, oil, steam, acidic medium, etc.
- Forged steel check valves are available in three cover connection designs: bolt-on cover, welded cover, and pressure self-tensioning cover.
Media Differences between ball valve and check valve
Media in Ball Valve
| Valve body material | Nominal pressure (MPa) | Working temperature (℃) | Applicable Media |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grey cast iron | ≤1.0MPa | -10℃-200℃ | Water, steam, air, gas and oil, etc. |
| Malleable Iron | ≤2.5MPa | -30℃-300℃ | Water, steam, air and oil |
| Ductile Iron | ≤4.0MPa | -30℃-350℃ | Water, steam, air and oil |
| Carbon Steel | ≤32.0MPa | -30℃-425℃ | Water, steam, air, hydrogen, nitrogen, nitrogen and petroleum |
| Copper Alloy | ≤2.5MPa | -40℃-250℃ | Water, seawater, oxygen, air, oil |
Media in Check Valve
| Valve body material | Nominal pressure (MPa) | Working temperature (℃) | Applicable Media | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon steel | 1.6-6.4 | ≤425 | Water, oil, steam | |
| 10.0-16.0 | ≤450 | |||
| Stainless steel | P | 1.6-16.0 | ≤200 | Nitric acid |
| R | 1.6-16.0 | ≤200 | Acetic acid | |
| Chromium-nickel-titanium steel | PI | 1.6-6.4 | ≤550 | Petroleum, petroleum products |
| Chromium-molybdenum steel | 1.6-16.0 | ≤550 | oil | |
Application Differences between ball valve and check valve
Ball valves are mainly used in petroleum, chemical and metallurgy.Ball valves are not recommended for use in applications involving pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and biological processing (except for chemical or non-sterile applications) because they are difficult to clean.
Check valves are used in many fluid systems such as chemical and power plants and in many other industrial processes. In aircraft and aerospace, check valves are used where high vibration, large temperature extremes and corrosive fluids are present. Check valves are also commonly used when multiple gases are mixed into a single gas stream. Check valves are installed on each individual gas stream to prevent the mixing of gases in the original gas stream.
Control Method Differences between ball valve and check valve

The opening and closing member of a ball valve is a ball with a circular passage, rotating around an axis perpendicular to the passage, and the ball rotates with the stem to open and close the passage. The ball valve can be closed tightly with only 90 degrees of rotation and a small torque.
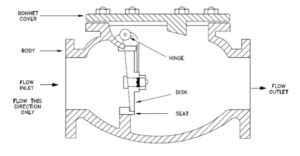
Check valve only allows the medium to flow in one direction, and to prevent the flow in the opposite direction. Usually this valve is automatic work, in one direction of flow of fluid pressure, the valve flap open; fluid flow in the opposite direction, by the fluid pressure and the self-weight of the valve flap combined flap act on the valve seat, thus cutting off the flow.
Which one is the best?
Ball valve advantages:
- Small fluid resistance.
- Simple structure, small size, light weight.
- Easy to operate, open and close quickly.
- Easy maintenance.
- Wide range of applications.
Ball valve disadvantages:
- Low temperature resistance level, can only be used in less than 180 ℃. Over this temperature, the sealing material will be aging.
- Its adjustment performance is relatively poor compared to the globe valve.
Check valve advantages:
- small size
- light weight
- simple structure.
Check valve disadvantages:
- The valve flap is easy to break; such as sealing surface damage.
- Easy to cause the media backflow.
Conclusion
Factors that may need to be considered when selecting a ball valve include the type of operation, housing material, circuit function, sealing, connection type and size, pressure, flow coefficient, temperature, and standard are critical.
Factors that may need to be considered when selecting a check valve include fluid compatibility, head loss, flow aspects, non-damping features, and total price.
In short, it is vital to consider the specifics of each installation while selecting a valve to ensure it works optimally. Contact a reliable industrial valve supplier for a wide range of valve types to meet your business needs.
Related Posts
-
How Duckbill Valves Reduce Energy Costs by 15-30% in Industrial Systems
-
Prominent Duckbill Valve Manufacturers in 2025
-
Industrial Duckbill Valve Pricing: Key Factors and Market Overview
-
The Application of Duckbill Valves in Urban Drainage Systems
-
China Duckbill Valve Industry Development Review and Prospect 2025
Leave a Message

Jack
Hi, I’m the author of this post, and I have been in this field for more than 10 years. If you want to get more info about duckbill check valves or others industrial valves, feel free to ask me any questions.